Runtime components
Page last updated:
This topic tells you about the Cloud Foundry Application Runtime runtime components.
Cloud Foundry components include a self-service application execution engine, an automation engine for application deployment, and lifecycle management, and a scriptable command line interface (CLI). Also, an integration with development tools to ease deployment processes. Cloud Foundry has an open architecture that includes a buildpack mechanism for adding frameworks, an application services interface, and a cloud provider interface.
See the following descriptions for more information about Cloud Foundry components. Some descriptions include links to more detailed documentation.
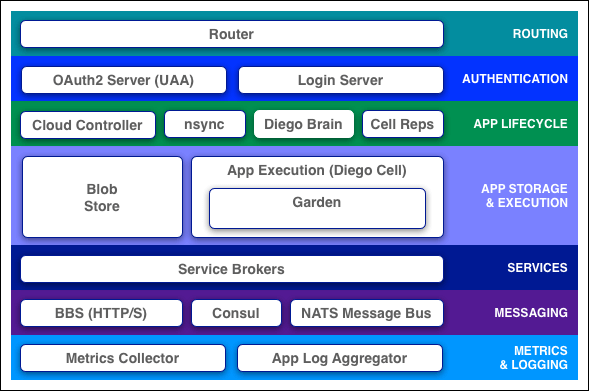
Routing
Router
The router routes incoming traffic to the appropriate component, either a Cloud Controller component or a hosted application running on a Diego Cell.
The router periodically queries the Diego Bulletin Board System (BBS) to determine which cells and containers each application currently runs on. Using this information, the router recomputes new routing tables based on the IP address of each cell virtual machine (VM) and the host-side port numbers for the cell’s containers.
For more information about the routing tier, including the router, see Cloud Foundry Routing Architecture.
Authentication
OAuth2 Server (UAA) and Login Server
The OAuth2 server (the UAA) and Login Server work together to provide identity management.
App Lifecycle
Cloud Controller and Diego Brain
The Cloud Controller (CC) directs the deployment of applications. To push an app to Cloud Foundry, you target the Cloud Controller. The Cloud Controller then directs the Diego Brain through the CC-Bridge components to coordinate individual Diego cells to stage and run applications.
The Cloud Controller also maintain records of orgs, spaces, user roles, services, and more.
nsync, BBS, and Cell Reps
To keep applications available, cloud deployments must constantly monitor their states and reconcile them with their expected states, starting and stopping processes as required.
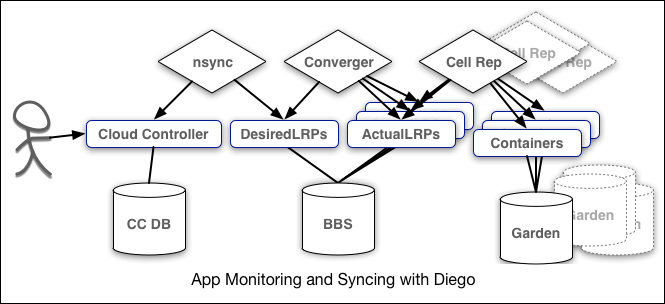
The nsync, BBS, and Cell Rep components work together along a chain to keep apps running. At one end is the user. At the other end are the instances of applications running on widely-distributed VMs, which might crash or become unavailable.
Here is how the components work together:
- nsync receives a message from the Cloud Controller when the user scales an app. It writes the number of instances into a
DesiredLRPstructure in the Diego BBS database. - BBS uses its convergence process to monitor the
DesiredLRPandActualLRPvalues. It runs or stops application instances as appropriate to ensure theActualLRPcount matches theDesiredLRPcount. - Cell Rep monitors the containers and provides the
ActualLRPvalue.
App Storage and Execution
Blobstore
The blobstore is a repository for large binary files, which Github cannot easily manage because GitHub is designed for code. The blobstore contains the following:
- Application code packages
- Buildpacks
- Droplets
You can configure the blobstore as either an internal server or an external S3 or S3-compatible endpoint.
Diego Cell
Application instances, application tasks, and staging tasks all run as Garden containers on the Diego Cell VMs. The Diego cell rep component manages the lifecycle of those containers and the processes running in them, reports their status to the Diego BBS, and emits their logs and metrics to Loggregator.
Services
Service Brokers
Applications typically depend on services such as databases or third-party SaaS providers. When a developer provisions and binds a service to an application, the service broker for that service is responsible for providing the service instance.
Messaging
Internal HTTPS and BBS
The component VMs of Cloud Foundry communicate with each other internally through HTTP and HTTPS protocols, sharing temporary messages and data stored in Diego’s Bulletin Board System (BBS).
BOSH Director colocates a BOSH DNS server on every deployed VM. All VMs keep up-to-date DNS records for all the other VMs in the same foundation, enabling service discovery between VMs. BOSH DNS also provides client-side load-balancing by randomly selecting a healthy VM when multiple VMs are available.
Diego’s Bulletin Board System (BBS) stores more frequently updated and disposable data such as cell and app status, unallocated work, and heartbeat messages, as well as longer-lived distributed locks. The BBS stores data in MySQL, using the Go MySQL Driver.
The route emitter component uses the NATS protocol to broadcast the latest routing tables to the routers.
Metrics and Logging
Loggregator
The Loggregator (log aggregator) system streams application logs to developers.
For more information about the Loggregator, see Loggregator Architecture.
Metrics Collector
The metrics collector gathers metrics and statistics from the components. Operators can use this information to monitor a Cloud Foundry deployment.
View the source for this page in GitHub