MongoDB Enterprise HA
Page last updated:
Integrating the Service With Your App
After the creation of the service and the binding of the service to the application, the environment variable VCAP_SERVICES is created. Information about the credentials are stored in this variable as shown here:
{
"mongodbent": [
{
"credentials": {
"database": "rs_a2215d2a-5b5d-0909-8d74-532982b72693",
"database_uri": "mongodb://3RlgLecirkFZxOxI:JYmPwXizSsyspGl0@a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693-0.service.consul:33694,a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693-1.service.consul:33694,a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693-2.service.consul:33694/rs_a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693?replicaSet=rs_a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693",
"host": "a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693-0.service.consul,a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693-1.service.consul,a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693-2.service.consul",
"ops_manager_password": "i7r240A3cTQkVMRdw7P4HCWirA2E2xzL!1aA",
"ops_manager_url": "http://opsmanager.service.consul:8080",
"ops_manager_user": "llYlttVLBe9T7lmL",
"password": "JYmPwXizSsyspGl0",
"port": "33694",
"replica_set": "rs_a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693",
"uri": "mongodb://3RlgLecirkFZxOxI:JYmPwXizSsyspGl0@a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693-0.service.consul:33694,a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693-1.service.consul:33694,a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693-2.service.consul:33694/rs_a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693?replicaSet=rs_a2215d2a-5b5d-4501-8d74-532982b72693",
"username": "3RlgLecirkFZxOxI"
},
"label": "mongodbent",
"name": "mongoentluk",
"plan": "small3rs",
"provider": null,
"syslog_drain_url": null,
"tags": []
}
]
}
Administrating Your MongoDB Enterprise Instances
To connect to a running MongoDB Enterprise instance with your local development tools, you can use the cf ssh feature of the cf CLI.
Sample Application
Cloud Foundry: Spring Music Example
Additional Databases
MongoDB Enterprise offers additional databases on the same replica set.
The first database is automatically initialized after creating the replica set. It can be accessed by creating bindings or service-keys on the mongodbent service instance.
A limited number of additional databases can be created on top of each MongoDB Enterprise replica set. To create an additional database you must first get the GUID of your replica set:
cf service my-mongodb-enterprise --guid
Then, create a database (where parent_reference is the GUID of your service instance):
On Linux:
cf create-service mongodbent-database default my-mongodb-enterprise-db -c '{ "parent_reference": "<MONGODBENTCLUSTER_GUID>" }'
On Windows PowerShell:
cf create-service mongodbent-database default my-mongodb-enterprise-db -c '{ \"parent_reference\": \"<MONGODBENTCLUSTER_GUID>\" }'
Please note that databases are competing for resources. Thus, you should limit the number of databases on your production replica sets.
Known limitations:
All bind and unbind operations of additional databases of the same cluster must happen sequentially.
Version Upgrade
MongoDB Enterprise service supports upgrading service instances to new versions.
CAUTION: Before upgrading your service, please carefully review the release notes and compatibility changes of newer version on the official MongoDB documentation.
Upgrading a Service Instance requires cf CLI v6.46.0+ and CAPI release 1.83.0+
MongoDB Enterprise service supports upgrading service instances to new versions.
To upgrade your service instances, do the following:
Confirm that an upgrade is available by running
cf servicesand reviewing theupgrade availablecolumn:$ cf services Getting services in org acceptance / space dev as admin... name service plan bound apps last operation broker upgrade available mydb mongodbent small create succeeded mongodb-broker yes otherdb mongodbent medium create succeeded mongodb-broker noUpgrade the service instance:
# cf-cli v6/v7 cf update-service mydb --upgrade # cf-cli v8 cf update-service mydbConfirm the operation:
You are about to update mydb. Warning: This operation may be long running and will block further operations on the service until complete. Really update service mydb? [yN]: y OK
We recommend creating a backup before evey upgrade, to prevent possible data loss. The preferred method is using backman.
Plan Upgrade
MongoDB Enterprise service instances can be upgraded to larger plans (downgrading to smaller plans is not possible).
The upgrade to a larger plan is done through the CF CLI by running the update service command.
cf update-service <service-name> -p <new-plan-name>
Caution: If your cluster is not running on the latest available MongoDB version in the marketplace, a plan upgrade will automatically trigger also a version upgrade (see chapter Version Upgrade for more details).
Ops Manager
As a MongoDB Enterprise customer, you receive access to the Ops Manager to see detailed performance metrics and health state.
To connect to the Ops Manager to get insights into your MongoDB, you can use the cf ssh feature of the cf CLI:
cf ssh -L 8080:opsmanager.service.consul:8080 myapp
After forwarding the port you can access Ops Manager under http://localhost:8080 in your browser and login with the Ops Manager user exposed to your application.
Specifications
Our MongoDB Enterprise offering consists of 3 dedicated VMs configured as a replica set.
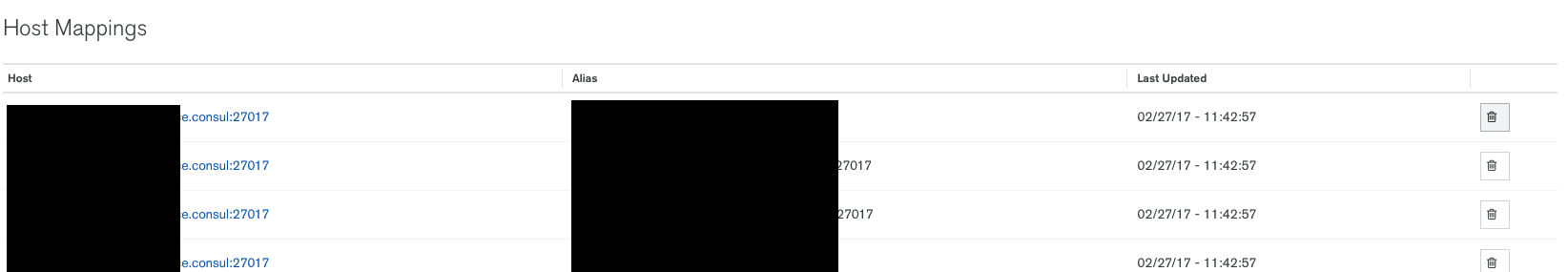
Ops Manager Host Mappings
There is a known bug regarding host mappings. When the deployment overview shows incorrect information, you need to delete the host mappings on http://opsmanager.service.consul:8080/v2/$GROUP_ID#deployment/hostMappingTab. Please replace $GROUP_ID with your actual group ID.
Permission Roles
On the MongoDB replica set you will receive the role readWrite@rs_DBNAME.
On the MongoDB Ops Manager you will receive the role Monitoring Admin.
Best Practices for Developers
- Write concern majority
Please read Replica Set Read and Write Semantics. We recommend a “Write Concern” of majority to avoid Rollbacks During Replica Set Failover.
- Check Ops Manager metrics regularly
Please check your Ops Manager metrics and graphs regularly. The performance statistics are particularly important after app deployments.
- Use an application driver maintained by the MongoDB team
It’s critical to find a driver that is well-maintained and stays up to date with the latest MongoDB features.
- Index early and often
Without question, the most common database performance issue is improper indexing (or a complete lack thereof). Have a look at Indexes docs.
- Consider a query timeout
MongoDB targets operations for termination if the associated cursor exceeds its allotted time limit. See cursor.maxTimeMS() for more details.
- Implement connection pool
It’s crucial to properly implement and manage the connections made from your app to the database. Please observe the number of connections via Opsmanager to see if connections are not closing correctly. Please also consider implementing connection pools in your app. You can find more information on this topic in the MongoDB documentation Create and Use a Connection Pool
Backup
If you want to create backups, and also be able to restore them afterwards, there is an app available that allows for automatic scheduled backups: backman - the appcloud backup manager.
Service instances bound to this app will be automatically backed up, can be downloaded and also restored on-demand.
If you have created additional databases on your cluster, each database must be bound to backman to be backed up.
Please make sure you create a backup, either by manually using mongodump yourself or with backman, before you do major changes to your database.
View the source for this page in GitHub