RabbitMQ
Page last updated:
Integrating the Service With Your App
After the creation of the service and the binding of the service to the application, the environment variable VCAP_SERVICES is created. Information about the credentials are stored in this variable as shown here:
{
"rabbitmqent": [
{
"credentials": {
"hostname": "rabbitmq.service.consul",
"hostnames": [
"rabbitmq-node-0.service.consul",
"rabbitmq-node-1.service.consul",
"rabbitmq-node-2.service.consul"
],
"http_api_uri": "http://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq.service.consul:15672/api",
"http_api_uris": [
"http://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-0.service.consul:15672/api",
"http://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-1.service.consul:15672/api",
"http://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-2.service.consul:15672/api"
],
"password": "rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW",
"protocols": {
"amqp": {
"host": "rabbitmq.service.consul",
"hosts": [
"rabbitmq-node-0.service.consul",
"rabbitmq-node-1.service.consul",
"rabbitmq-node-2.service.consul"
],
"password": "rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW",
"port": 5672,
"ssl": false,
"uri": "amqp://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq.service.consul/bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264",
"uris": [
"amqp://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-0.service.consul/bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264",
"amqp://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-1.service.consul/bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264",
"amqp://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-2.service.consul/bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264"
],
"username": "i0zRgICRqzDB5fll",
"vhost": "bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264"
},
"management": {
"host": "rabbitmq.service.consul",
"hosts": [
"rabbitmq-node-0.service.consul",
"rabbitmq-node-1.service.consul",
"rabbitmq-node-2.service.consul"
],
"password": "rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW",
"path": "/api",
"port": 15672,
"ssl": false,
"uri": "http://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq.service.consul:15672/api",
"uris": [
"http://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-0.service.consul:15672/api",
"http://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-1.service.consul:15672/api",
"http://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-2.service.consul:15672/api"
],
"username": "i0zRgICRqzDB5fll"
},
"mqtt": {
"host": "rabbitmq.service.consul",
"hosts": [
"rabbitmq-node-0.service.consul",
"rabbitmq-node-1.service.consul",
"rabbitmq-node-2.service.consul"
],
"password": "rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW",
"port": 1883,
"ssl": false,
"uri": "mqtt://bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264%3Ai0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq.service.consul",
"uris": [
"mqtt://bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264%3Ai0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-0.service.consul",
"mqtt://bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264%3Ai0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-1.service.consul",
"mqtt://bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264%3Ai0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-2.service.consul"
],
"username": "bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264:i0zRgICRqzDB5fll"
},
"stomp": {
"host": "rabbitmq.service.consul",
"hosts": [
"rabbitmq.service.consul",
"rabbitmq-node-0.service.consul",
"rabbitmq-node-1.service.consul",
"rabbitmq-node-2.service.consul"
],
"password": "rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW",
"port": 61613,
"ssl": false,
"uri": "stomp://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq.service.consul",
"uris": [
"stomp://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-0.service.consul",
"stomp://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-1.service.consul",
"stomp://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-2.service.consul"
],
"username": "i0zRgICRqzDB5fll",
"vhost": "bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264"
}
},
"ssl": false,
"uri": "amqp://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq.service.consul/bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264",
"uris": [
"amqp://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-0.service.consul/bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264",
"amqp://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-1.service.consul/bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264",
"amqp://i0zRgICRqzDB5fll:rvUgjRjnMa6mejiW@rabbitmq-node-2.service.consul/bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264"
],
"username": "i0zRgICRqzDB5fll",
"vhost": "bd0c989a-8a16-4641-8bcc-70a99c7c7264"
},
"label": "rabbitmqent",
"name": "testrabbit",
"plan": "usage",
"tags": []
}
]
}
Offered protocols and plugins
RabbitMQ provides the following protocols which are all exposed in VCAP_SERVICES:
- AMQP
- MQTT
- STOMP
- HTTP (API and management interface)
The application should only use the uri or hostname properties of the desired protocol within VCAP_SERVICES to achieve proper loadbalancing.
These properties contain rabbitmq.service.consul so the connection is established to a HAProxy that automatically distributes requests to all available RabbitMQ nodes.
The alternative properties uris and hostnames should only be used if single nodes need to be targeted explicitly.
This can be used to achieve slightly better performance by connecting publishers and subscribers to the queue master node.
However, this comes with a serious disadvantage, since the connections fail in case the single node goes down.
The full list of exposed plugins:
rabbitmq_consistent_hash_exchangerabbitmq_event_exchangerabbitmq_managementrabbitmq_management_agentrabbitmq_mqttrabbitmq_prometheusrabbitmq_shovelrabbitmq_shovel_managementrabbitmq_stomprabbitmq_web_dispatch
Advanced configuration
In most cases, connecting your applications to the loadbalanced service is completely sufficient. For some high end setups, getting the last drop of performance and scalability from the cluster is an advanced task and might include strategies which need more logic on the client side:
Non-HA queues
By default, every queue created on RabbitMQ is created on one node (the queue master) and is replicated to other nodes to achieve high availability.
In certain cases, high availability is sacrificed to avoid the overhead of replication to achieve higher performance. For this, just create the queue with the prefix appcloud-non-ha and it will not be replicated to other nodes.
Queue Limits
In shared cluster environments, in order to protect the clusters from the sometimes unintentional “noisy neighbor” effect it is advisable to configure limits on the queues.
Such limitations are already in place using Operator Policies (see Limitations) and they will take precedence. As these operator policies were only applied on a newer generation of vhosts, some older vhosts don’t benefit from this configuration. Recreating a RabbitMQ service instance will create a vhost using the latest configuration. Sometimes this is not possible in production environments. In such situation the limits can be configured using:
- user policies configured on the vhost level
- optional arguments on the queue level
The recommended way is to use policies, as they are scoped per vhost and are dynamically for all matching queues. See how policies work (including examples) on the RabbitMQ documentation page.
A more concrete example using the HTTP API can be used for the older generation vhosts. This policy named user-queue-limits captured all (.*) queues and sets the maximum queue length (max-length) to 100'000 messages, the maximum queue size (max-length-bytes) to 100 MB and the time-to-live (message-ttl) for the messages in the queue to 14 days:
PUT /api/policies/<your-vhost-uuid>/user-queue-limits
{
"pattern": ".*",
"definition": {
"max-length": 100000,
"max-length-bytes": 104857600,
"message-ttl": 1209600000
},
"priority": 1,
"apply-to": "queues"
}
For more details see the RabbitMQ documentation.
Consistent Hash exchange
For a different approach to scale your queues on the cluster, the Consistent hash exchange plugin is enabled.
Limitations
The RabbitMQ service enforces some limitations to ensure the cluster’s performance.
Per-Queue Message TTL of 14 days
To protect the cluster’s disk from filling up with old messages that were never picked up, the per-queue message TTL is set to 14 days. Messages that are in the queue for longer than 14 days are automatically discarded.
Operator Policies
The RabbitMQ cluster implements operator policies to set certain limits on queues and messages. The following operator policies are defined:
max-length: 100’000: If a queue holds 100'000 messages, the most recently published messages will be discarded.max-length-bytes: 100MB: If a queue holds more than 100MB of message data, the oldest messages are discarded from the head of the queue.
Connection Limits
To avoid high load caused by too many open connections, a limit on service instance level is implemeted. A single service instance can hold a maximum of 500 connections. Once this limit is reached, all further connections will be terminated.
Managing your RabbitMQ instances
To get access to the RabbitMQ management console, you can use the cf ssh command. Here’s how it works:
- You’ll need to use an app as a host for SSH-ing. Any running app will do. If you don’t have one yet, push a default app through the web console
- Create a service key for your RabbitMQ instance with
cf create-service-key <service-name> manage(replace the term in<>with your service’s name) - Look at the service key’s credentials with
cf service-key <service-name> manage - SSH into your app with
cf ssh -L 13000:<credentials.hostname>:<credentials.management_port> <app-name>(replace the values in<>with the actual values from the service key and with your app’s name) - Open your browser and visit http://localhost:13000 and use
<credentials.username>and<credentials.password>from your service key as the credentials - When you’re done, simply close the terminal window with the open SSH connection
Sample Application
Cloud Foundry: RabbitMQ Example
Best Practices
Queues
Keep queues short
RabbitMQ queues work fast and reliably when the they’re empty / have only a few messages queued up. RabbitMQ is not designed to hold message over a long period of time and it should always be the goal to keep the queues empty. Not only does this minimise the risk of message loss, it also increases the overall stability of the cluster and its performance.
Know when to use lazy queues
Lazy queues are queues that save their messages to disk to achieve some persistency. This has a negative impact on the performance of the specific queue but more predictable performance overall when as it minimises memory usage. Small and fast queues should (in general) not be declared as lazy queues. For large queues that don’t require a fast throughput, lazy queues are advised. Lazy queues are enabled by default on the Application Cloud RabbitMQ service offering.
Auto-delete queues
Queues will remain forever on the cluster by default (even when they’re not active). This will put unnecessary strain on the cluster. To free up resources and don’t run into limits, queues should be declared with the auto-delete flag set to true. With this, the queues will be deleted as soon as there are no more active connections using them.
Connections
General
Connections in RabbitMQ use up a lot of memory. In order to keep the cluster healthy and fast, it is important that there are as few open connections as possible. This can be achieved by keeping connections open for client applications. A good practice is to keep the connection open throughout the lifetime of the client application.
Auto reconnect
Connections between client applications and the RabbitMQ cluster are stable for the most part. However, it’s possible that a network outage can occur or the cluster has an unexpected downtime. In such a case, the client application usually needs to reconnect to the cluster and reopen connections and channels. To automate this process, most RabbitMQ Client APIs support the auto-reconnect feature (see the Java Client API for an example). It is advised to enable the auto-reconnect feature on the client applications.
Channels
General
Channels share the same as restrictions as connections - they can use up quite a lot of memory if opened and closed frequently. Although less memory is used when creating a channel, it’s still recommended that channels are kept open for a long time.
Threads
Channels are not thread safe and should not be shared between different threads.
Prefetch
RabbitMQ allows the for the control over how many messages are sent to the consumer at the same time. Per default, the prefetch value is sent to unlimited, meaning the server tries to send as many messages as possible at the same time. Setting a proper prefetch value can help to achieve the desired performance of the service. If the prefetch count is set too low, the server while idle and wait for more the client to send more message. On the other hand, if the prefetch count is too high the client might take a long time to consume the messages.
Setting the correct prefetch value depends on the setup of the client application. As such, there is not one prefetch value that is best for all cases. As a general rule the prefetch count should be higher if there is only one / few consumers that consume messages quickly. If the client application feature many consumers, a lower prefetch value should be set. More information can be found here: https://www.rabbitmq.com/docs/3.13/consumer-prefetch.
Messages
Message size
Large messages can take up a lot of resources and should generally be avoided. RabbitMQ is designed for high message throughput and as such it is better to keep the messages sent over RabbitMQ small. Splitting up large payloads into smaller message should be considered when designing the client application.
Message ack’s and confirms
RabbitMQ features acknowledgments (ack’s) for receiving message and publisher confirms (confirms) for sending messages. These mechanisms can be used to ensure that a message has been send / received correctly. Ack’s and confirms are generally a good idea to implement as they increase the reliability and consistency of the message flow.
Note: Ack’s and confirms have a small performance impact.
Backups and Restore
RabbitMQ contains two types of data: definitions (metadata, schema/topology) and messages. Our backup system takes care of saving only the definitions, but not the messages. The reason for this is that messages are short-lived, transient in nature, and RabbitMQ is not designed as a data storage solution. The automated backups for the definitions are stored in an encrypted, environment-specific S3 bucket for 30 days. This is done by the backman component every 12 hours.
The restoration process is manual and requires intervention from the RabbitMQ operations team; therefore it will only be performed for disaster recovery cases. All nodes in the cluster must be restored together and all customers will be affected, which means that it is not possible to restore a backup for a single cluster node or a single customer.
Migration to Quorum Queues
Quorum Queues
Quorum Queues are a superior replacement for Classic Mirrored Queues that were introduced in RabbitMQ version 3.8. And there are two complementary reasons why you would need to migrate:
- Classic Mirrored Queues were deprecated in 3.9 and will be completely removed in 4.0
- they are more reliable and predictable, faster for most workloads and require less maintenance
Quorum Queues are better in all regards, but they are not 100%-compatible feature-wise with Mirrored Queues.
How to Make Use of Quorum Queues
Declare a queue by setting the x-queue-type argument to quorum. This will declare a quorum queue with three replicas.
After declaring a quorum queue, you can bind it to any exchange just as with other queue types.
How to Migrate to Quorum Queues from Classic Mirrored Queues
Directly changing queue types is not possible. Instead, there are two options when moving from classic mirrored queues to quorum queues:
Option 1: Create a new queue with the type quorum and move the publisher, then the consumer.
- Declare a Quorum Queue: Set the
x-queue-typequeue argument toquorum. The queue argument should be provided by the client and set when declaring the queue. - Move the publisher and empty the queue: Empty the queue by moving the publisher to the new queue and allowing the consumer to consume messages from the old queue until it’s empty.
- Move the consumer: Finally, switch the consumer to the new queue.
Option 2: Move messages from the old queue to the new queue by using a shovel.
- Set up a shovel: Create a shovel from the RabbitMQ management interface. Click on the Admin tab and select Shovel Management from the dropdown menu.
- Declare quorum queues: Set the x-queue-type queue argument to quorum . The queue argument should be provided by the client and set when declaring the queue.
- Move messages: Use the created shovel to move messages from one queue to the other.
Compatibility considerations
The RabbitMQ documentation has a dedicated page on Quorum Queues. Specifically, in this document there is a feature matrix which provides a list with all differences between Mirrored Classic Queues and Mirrored Queues. These differences can require a different amount of work for a successful migration. Some of them can be trivial to change, while others can require changes in the way an application interacts with RabbitMQ.
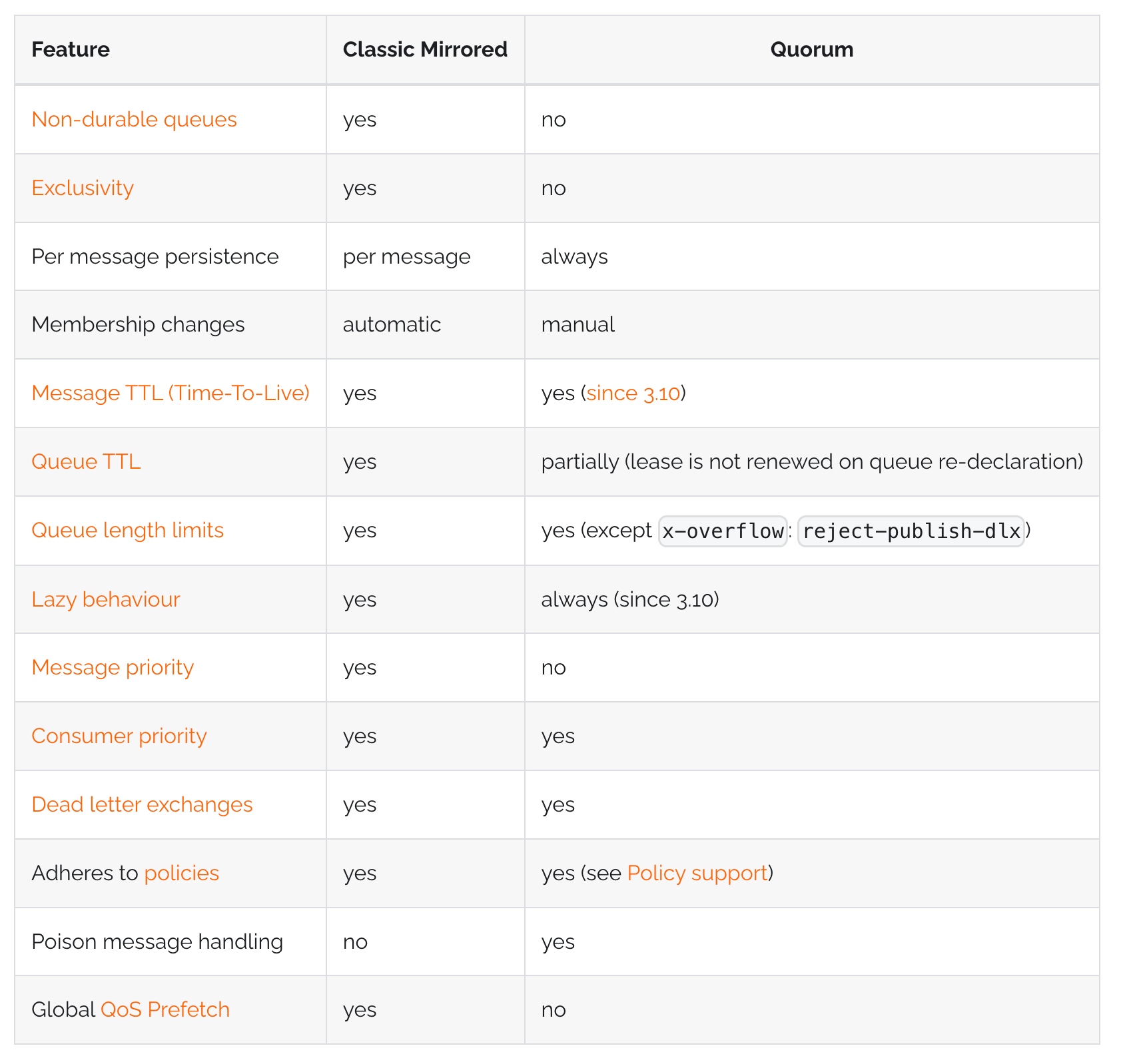
Breaking changes
Priority queues
Classic mirrored queues actually create a separate queue for every priority behind the scenes. For migration it’s necessary for the applications to explicitly handle creation of those queues, and also publishing/consuming to and from them.
Overflow dead lettering
Overflow mode reject-publish-dlx is not supported by quorum queues. The code needs to be updated to use publisher confirms and to do dead lettering by itself.
Global QoS for consumers
Global QoS for consumers is not supported for quorum queues. A decision needs to be made about how necessary results can be achieved using alternative means, e.g. by using a lower per-consumer QoS that can give approximately the same results (given the known application load pattern).
x-cancel-on-ha-failover for consumers
Mirrored queues consumers can be automatically cancelled when a queue leader fails over. This can cause a loss of information about which messages were sent to which consumer, and redelivery of such messages.
Quorum queues are less exposed to such behaviour - the only case when it still can happen is when a whole node goes down. For other leader changes (e.g. caused by rebalancing), there will be no redeliveries.
And redeliveries can also happen for inflight messages when the consumer is cancelled or the channel is closed. So application needs to be prepared for redeliveries anyway, without specifically asking for such information.
Trivial Changes
Lazy queues
Classic queue can optionally operate in lazy mode, but for quorum queues this is the only way of operation.
Non-durable queues
Non-durable queues will be deleted on a node/cluster boot.
Non-durable queues concept is also going away in the future releases: the only option for ephemeral queues will be exclusive queues. This affects only durability of queue definitions, messages can still be marked transient.
For such queues a decision has to be made one way or another: is this queue content important enough to get availability guarantees of quorum queues, or it’s better to downgrade it to a classic (but durable) queue.
Exclusive queues
Exclusive queues are not mirrored even if the policy says so. But attempt to declare an exclusive quorum queue will result in an error.
This is clearly one of the cases where migration is not needed, but care must be taken as to avoid exclusive queue declarations with an explicit x-queue-type: quorum argument.