Cloud Foundry routing architecture
Page last updated:
This topic tells you about the routing architecture and flow in Cloud Foundry Application Runtime.
Routing architecture components
The following summarizes the roles and responsibilities of various components depicted in the Cloud Foundry routing architecture diagrams. These summaries are limited to the roles and responsibilities these components have pertaining to routing. For more complete descriptions of these components, see Cloud Foundry Concepts, Cloud Foundry Components, and Diego Components and Architecture.
| Component Name | Summary |
|---|---|
| BOSH manifest | Used to configure route registrar with route(s) for system components such as UAA and Loggregator. |
| Cloud Controller | Contains route metadata, including whether they are HTTP or TCP. |
| Diego BBS | Contains IP and port metadata as well as route metadata from Cloud Controller, which route emitter discovers. |
| Diego cell | Manages app instances and tasks and long-running processes related to them. A route emitter runs on each cell. |
| Gorouter | Routes HTTP traffic coming into Cloud Foundry to the appropriate component. Receives route updates through NATS. Routes that have not been updated in two minutes are pruned from the Gorouter’s database. |
| NATS | Receives routing configuration from route emitter and provides same to Gorouter. |
| Route registrar | Sends routing metadata described in BOSH manifest for system components such as UAA and Loggregator to NATS. This is because the Diego cell does not have information about system components, only about user spaces. |
| Route emitter | Periodically emits route, IP, and port metadata to NATS or Routing API as registration and unregistration messages. Does not know about app instances on Diego cell, but knows what cell it belongs to and learns about what app instances are running on its cell by asking Diego BBS for information about app instances on the same cell. |
| Routing API | Receives routing configuration from route emitter and other internal clients, and provides routing configuration for TCP router. |
| Routing database | Saves some routing data from Routing API. If the Gorouter misses a message about an unmapped route from NATS, it does not get it again, so TCP router and Routing API can consult routing database for current state of routes. |
| TCP router | Routes TCP traffic coming into Cloud Foundry to the appropriate component. Receives route updates through the routing API. |
| HealthChecker | An executable designed to perform TCP/HTTP-based health checks of processes managed by monit in BOSH releases. Because the version of monit included in BOSH does not support specific TCP/HTTP health checks, this utility is designed to perform health checking, and restart processes if they become unreachable. |
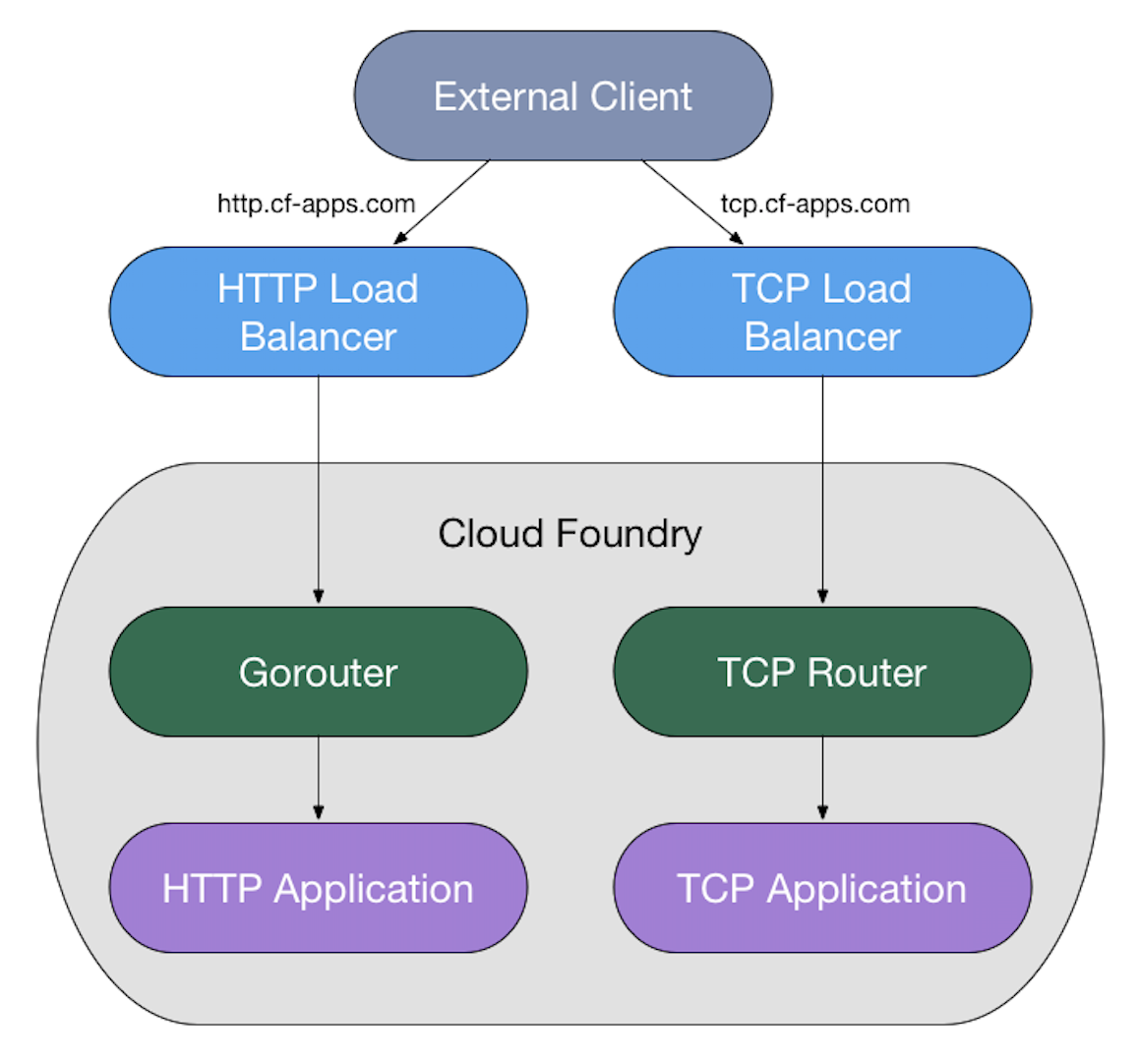
Making a request to external client
The following process tells you about how an external client makes a request to an app running on Cloud Foundry:
The external client sends its request.
Your DNS service sends the request to the HTTP or TCP load balancer based on the prefix of the DNS name in the client request, such as
httpinhttp.example.com.The load balancer sends the request to the load balancer’s corresponding router.
The router sends the request to the app.
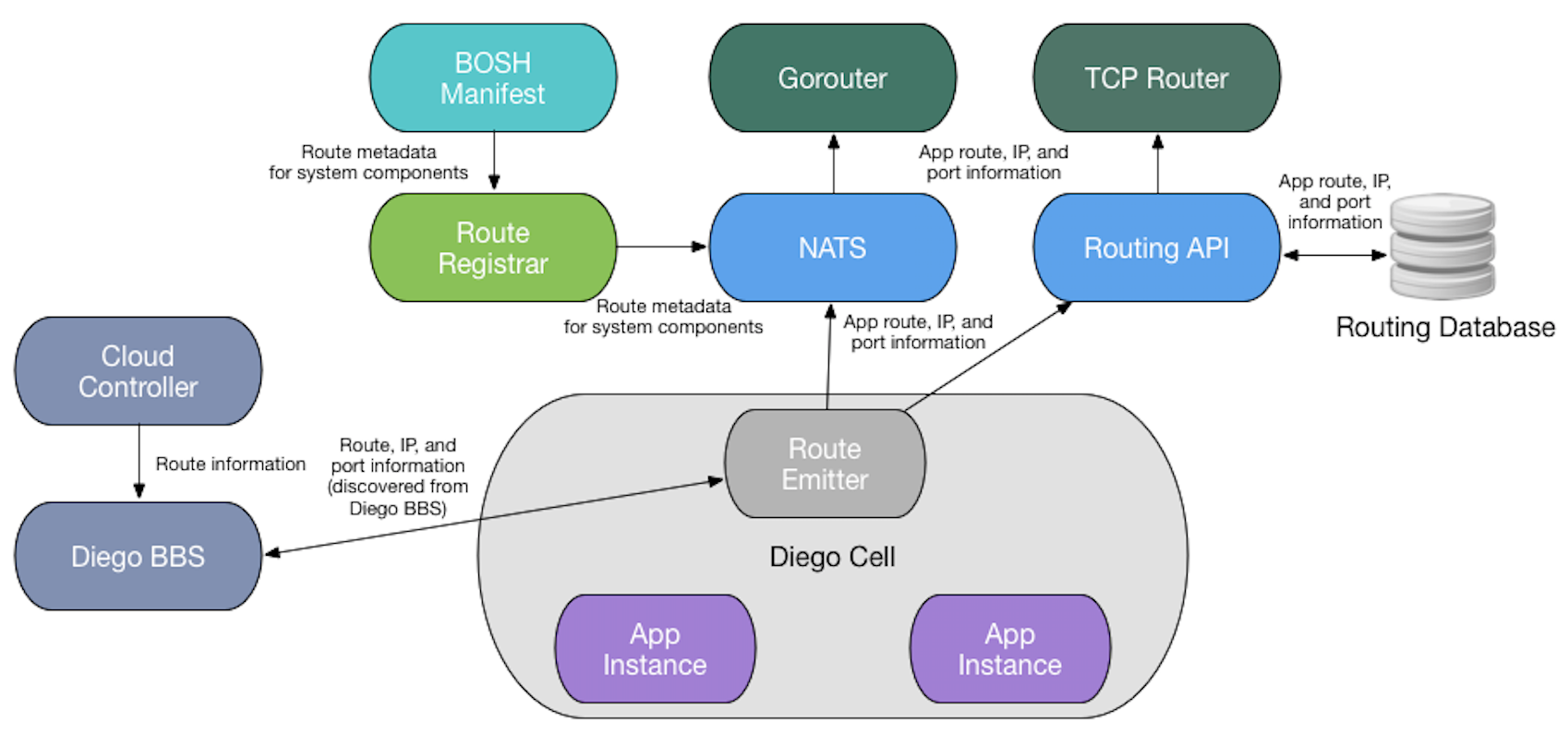
Maintaining updated routing tables
Because each app can have many instances, one app route can go to multiple containers. As Diego moves and scales app instances, the route emitter on each cell sends messages to NATS or the Routing API to register and deregister routes to the cell’s app instances.
The route emitter periodically emits the routes it discovers from Diego BBS to NATS and the Routing API as registration and unregistration messages every twenty seconds. The Gorouter and TCP router use TLS to verify app identity and confirm that its routes are up-to-date. For more information about how Cloud Foundry maintains route consistency, see Preventing Misrouting in HTTP Routing.
The following process describes how a router obtains information about routes for an app running on Cloud Foundry:
Cloud Controller component sends app route information to Diego BBS. For HTTP routing, route information includes the host and path of an external URL, as shown in the format of the
router.registermessage in the Gorouter documentation on GitHub. For TCP routing, route information includes the route port on which the TCP connection was received; for more information, see the Routing API documentation on GitHub.Diego BBS coordinates the back end IP address and port where each instance of the app runs. When queried by the route emitter, the BBS sends this information along with the Cloud Controller app route information to the route emitter on the Diego cell where instances of the app are located.
If a route is HTTP, the route emitter on the Diego cells sends app route, IP, and port information to NATS, which then sends it to the Gorouter. If a route is TCP, the route emitter sends that information to the Routing API, which then sends it to the TCP router.
Gorouter and TCP router use the route, IP, and port information from the route emitter to map incoming app requests to back end app instance locations.
Routing table recovery after component failure
Cloud Controller and Diego BBS have their own databases, while NATS and the Gorouter only store their data in memory. If NATS or the Gorouter are restarted, they lose all of their data and must wait for the route emitter to send data to them again. If Diego BBS is restarted, it can retrieve its data from Cloud Controller.
If Cloud Controller is restarted, you must retrieve its data from a backup.
View the source for this page in GitHub